The best meteor showers are a spectacular sight but, unfortunately, 2021 starts with a whimper. Moonlight this January will wash out the first of the big three — the Quadrantids (seen above in 2020).
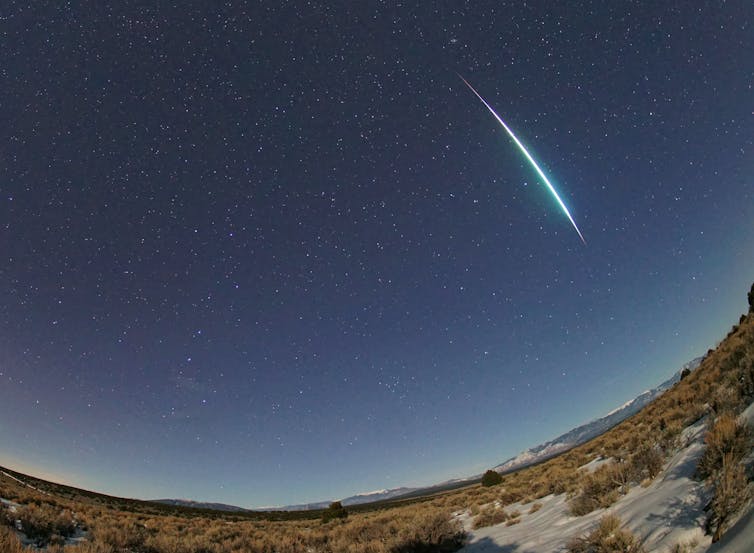

After that, the year just gets better and better, with the Perseids (another of the big three along with the Geminids) a particular highlight for northern hemisphere observers in August.
In addition to the year’s other reliable performers we’ve included one wild card: the Aurigids, in late August. Most years, the Aurigids are a very, very minor shower, but they just might put on a show this year.
So here is our pick of the meteoric highlights for 2021.
For each meteor shower, we give you a finder chart showing the radiant (where the meteors appear to come from in the sky) and where best to look in the sky, the full period of activity and the forecast peak. Most meteor showers typically only yield their best rates for about a day around maximum, so the peak night is definitely the best to observe.
The Zenithal Hourly Rate ZHR is the maximum number of meteors you would expect to see under perfect observing conditions. The actual number you will see will likely be lower.
Most meteor showers can only really be observed from either the northern [N] or southern [S] hemisphere, but a few are visible from both [N/S].
Lyrids [N/S; N favoured]
Active: April 14–30
Maximum: April 22, 1pm UTC = 11pm AEST (Qld) = 7am CST = 3am Hawaii time
ZHR: 18
Parent: Comet C/1861 G1 Thatcher
The Lyrids are one of the meteor showers with the longest and most storied histories, with recorded observations spanning millenia. In the past, they were one of the year’s most active showers, with a history of producing spectacular meteor storms.
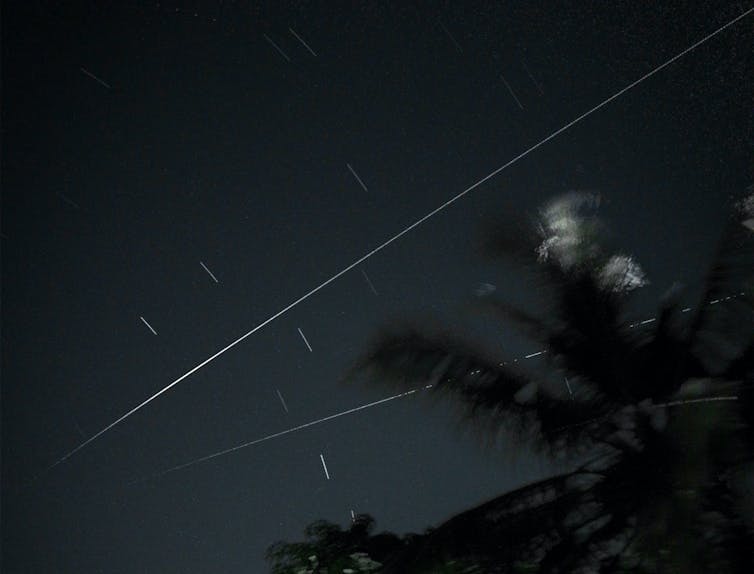

Flickr/DraconianRain, CC BY-NC
Nowadays, the Lyrids are more sedate, putting on a reliable show without matching the year’s stronger showers. They still throw up occasional surprises such as an outburst in excess of 90 meteors per hour in 1982.
This year’s peak Lyrid rates coincide with the first quarter Moon, which will set around midnight, local time, for most locations. The best time to observe will come in the early hours of the morning, after moonset.
For observers in the northern hemisphere, the Lyrid radiant will already be at a useful altitude by the time the Moon is low in the sky, so some brighter meteors might be visible despite the moonlight in the late evening (after around 10:30pm, local time).
Once the Moon sets the sky will darken and make the shower much easier to observe, yielding markedly higher rates.
For observers in the southern hemisphere, the Lyrid radiant reaches a useful altitude in the early hours of the morning, when the Moon will have set. If you’re a keen meteor observer, it could be worth setting your alarm early to get out and watch the show for a few hours before dawn.
Lyrid meteors are fast and often quite bright so can be rewarding to observe, despite the relatively low rates (one every five or ten minutes, or so). Remember, this shower always has the potential to throw up an unexpected surprise.
Eta Aquariids [S]
Active: April 19–May 28
Maximum: May 6, 3am UTC = 1pm AEST (Qld/NSW/ACT/Vic/Tas) = 11am AWST (WA)
ZHR: 50+
Parent: Comet 1P/Halley
The Eta Aquariids are an autumn treat for southern hemisphere observers. While not one of the big three, they stand clear as the best of the rest of the annual showers, yielding a fine display in the two or three hours before dawn.
The Eta Aquariids are fast meteors and are often bright, with smoky trains. They are fragments of the most famous comet, 1P/Halley, which has been laying down debris around its current orbit of the Sun for tens of thousands of years.
Earth passes through that debris twice a year, with the Eta Aquariids the best of the two meteor showers that result. The other is the Orionids, in October.
Where most meteor showers have a relatively short, sharp peak, the Eta Aquariids remain close to their best for a whole week, centred on the maximum. Good rates (ZHR > 30 per hour) should be visible before sunrise on each morning between May 3–10.
The Moon will be a waning crescent when the Eta Aquariids are at their best. Its glare should not interfere badly with the shower, washing out only the faintest members.
Observers who brave the pre-dawn hours to observe the Eta Aquariids will have the chance to lie beneath a spectacular sky. The Milky Way will be high overhead, with Jupiter, Saturn and the Moon high to the east and bright, fast meteors streaking across the sky from an origin near the eastern horizon.
Perseids [N]
Active: July 17–August 24
Maximum: August 12, 7pm–10pm UTC = 8pm–11pm BST = August 13, 4am–7am JST
ZHR: 110
Parent: Comet 109P/Swift-Tuttle
The Perseids are the meteoric highlight of the northern summer and the most observed shower of the year. December’s Geminids offer better rates but the timing of the Perseid peak makes them an ideal holiday treat.
The Perseids are debris shed behind by comet 109P/Swift-Tuttle, which is the largest known object (diameter around 26km) whose orbit currently intersects that of Earth.
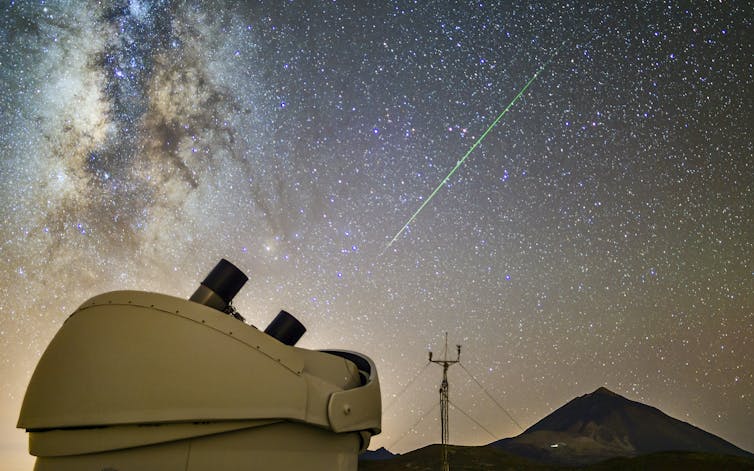

Flickr/StarryEarth, CC BY-NC
Perseid meteors are fast, crashing into Earth at a speed of about 216,000km/h, and often bright. While the shower is active, at low levels, for more than a month, the best rates are typically visible for at the three nights centred on the peak.
For observers at European latitudes, the Perseid radiant rises by mid-evening, so the shower can be easily observed from 10pm local time, and remains high all through the night. The later in the night you look, the higher the radiant will be and the more meteors you’re likely to see.
Aurigids [N favoured]
Active: August 28–September 5
Maximum: Potential Outburst on August 31, peaking between 9:15pm–9:40pm UTC = 10:15pm–10:40pm BST = 11:15pm–11:40pm CEST = September 1, 1:15am–1:40am Gulf Standard Time = September 1, 5:15am–5:40am AWST (WA)
ZHR: 50–100 (?)
Parent: Comet C/1911 N1 Kiess
Where the other showers are reliable and relatively predictable, offering good rates every year, the Aurigids are an entirely different beast.
In most years, the shower is barely visible. Even at its peak, rates rarely exceed just a couple of meteors seen per hour. But occasionally the Aurigids bring a surprise with short and unexpected outbursts of 30-50 meteors an hour seen in 1935, 1986, 1994 and 2019.
The parent comet of the Aurigids, C/1911 N1 Kiess, moves on an orbit with a period far longer than the parent of any other shower on our list.
It is thought the orbit takes between 1,800 and 2,000 years to complete, although our knowledge of it is very limited as it was only observed for a short period of time.
In late August every year, Earth passes through debris shed by the comet at a previous passage thousands of years into the past. In most years, the dust we encounter is very sparse.
But occasionally we intersect a denser, narrow stream of debris, material laid down at the comet’s previous passage. That dust has not yet had time to disperse so is more densely packed and hence gives enhanced rates: a meteor outburst.
Several independent research teams studying the past behaviour of the shower have all come to the same conclusion. On August 31, 2021, the Earth will once again intersect that narrow band of debris and an outburst may occur, with predictions it will peak around 21:17 UTC or 21:35 UTC.
Such an outburst would be short-lived. The dense core of the debris stream is so narrow it will take the Earth just ten or 20 minutes to traverse. So you’ll have to be lucky to see it.
The forecast outburst this year is timed such that observers in Eastern Europe and Asia will be the fortunate ones, with the radiant above the horizon. The waning Moon will light the sky when the radiant is above the horizon, washing out the fainter meteors from the shower.
The Aurigids tend to be fast and are often quite bright. Previous outbursts of the shower have featured large numbers of bright meteors. It may just be worth getting up and heading outside at the time of the predicted outburst, just in case the Aurigids give us a show to remember.
Geminids [N/S]
Active: December 4–17
Maximum: December 14, 7am UTC = 6pm AEDT (NSW/ACT/Vic/Tas) = 3pm AWST (WA) = 2am EST
ZHR: 150
Parent: Asteroid 3200 Phaethon
The Geminid meteor shower is truly a case of saving the best until last. By far the best of the annual meteor showers, it graces our skies every December, yielding good numbers of spectacular, bright meteors.
The shower is so good it is always worth observing, even in 2021, when the Moon will be almost full.
Over the decades, the Geminids have gradually become stronger and stronger. They took the crown of the year’s best shower from the Perseids in the 1990s, and have continued to improve ever since.
For observers in the northern hemisphere, the Geminids are visible from relatively early in the evening, with their radiant rising shortly after sunset, and remaining above the horizon for all of the hours of darkness.
As the night progresses, the radiant gets very high in the sky and the shower can put on a truly spectacular show.
For those in the southern hemisphere, the situation is not quite as ideal. The further south you live, the later the radiant will rise, and so the later the show will begin.
When the radiant reaches its highest point in the sky (around 2am–3am local time), it sits closer to the horizon the further south you are, so the best meteor rates you observe will be reduced compared to those seen from more northerly locations.
Despite these apparent drawbacks, the Geminids are still by far the best meteor shower of the year for observers in Australia, and are well worth a look, even on the moonlit nights of 2021.
Peak Geminid rates last for around 24 hours, centred on the official peak time, before falling away relatively rapidly thereafter. This means that observers around the globe can enjoy the display.
The best rates come when the radiant is highest in the sky (around 2–3am) but it is well worth looking up at any time after the radiant has risen above the horizon.
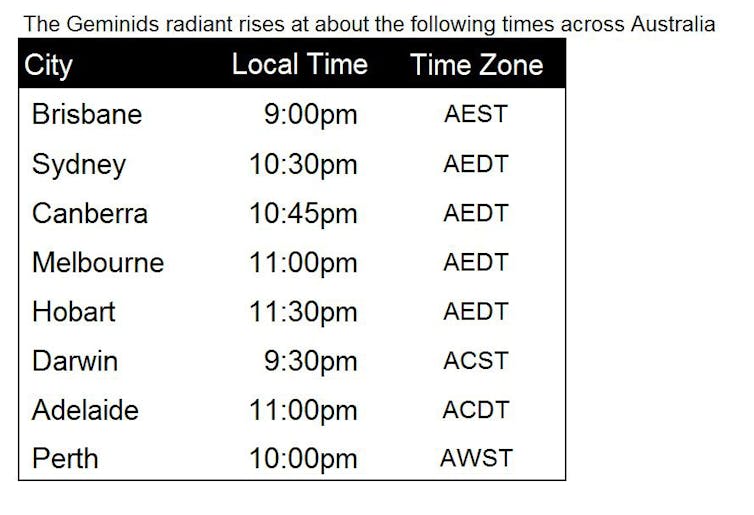
So wherever you are on the planet, if skies are clear for the peak of the Geminids, it is well worth going outside and looking up, to revel in the beauty of the greatest of the annual meteor showers.![]()
Jonti Horner, University of Southern Queensland and Tanya Hill, Museums Victoria
Jonti Horner, Professor (Astrophysics), University of Southern Queensland and Tanya Hill, Honorary Fellow of the University of Melbourne and Senior Curator (Astronomy), Museums Victoria
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.